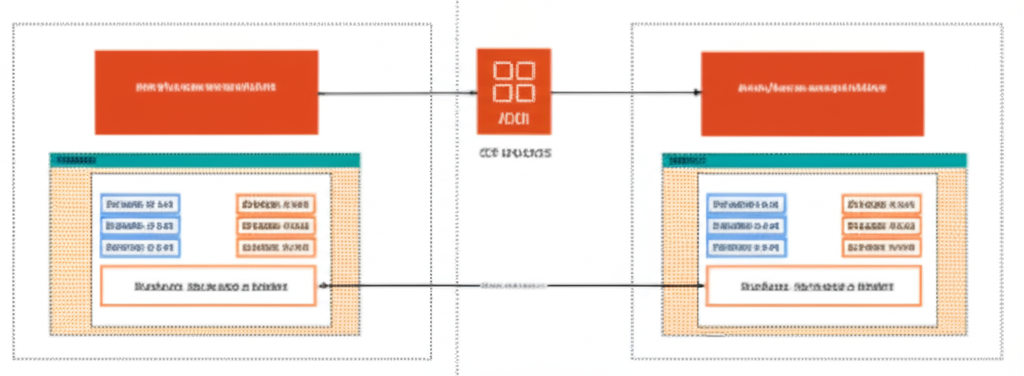
Designing Robust Multi-Region Disaster Recovery on AWS
Ensuring business continuity in the face of unforeseen events is paramount for any organization. Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides a robust and flexible platform for designing sophisticated disaster recovery (DR) strategies. This post delves into the intricacies of designing a resilient multi-region DR plan on AWS, focusing on clarity, practical examples, and actionable insights for advanced users.
Understanding Multi-Region DR: The Ultimate Safety Net
Think of your AWS infrastructure as a vital set of organs. A single-region DR strategy is like having a backup organ within the same body – if a localized issue occurs, the backup can take over. Multi-region DR, however, is like having a completely separate, identical body in a different geographical location. If a major disaster affects one region, your entire infrastructure can seamlessly switch over to the other, minimizing downtime and data loss.
Why Multi-Region DR?
While single-region DR offers significant improvements over no DR plan, multi-region deployments provide enhanced resilience against:
- Large-scale regional outages: Natural disasters, widespread power failures, or major network disruptions can impact entire AWS regions.
- Data sovereignty and compliance: Some regulations might require data to be replicated across geographically distant locations.
- Minimizing Recovery Point Objective (RPO) and Recovery Time Objective (RTO): By having a standby environment in another region, you can achieve near-zero RPO and RTO for critical applications.
Key Concepts and Strategies
Designing an effective multi-region DR strategy involves several key considerations:
- Recovery Objectives (RPO/RTO): Clearly define your RPO (the maximum acceptable amount of data loss) and RTO (the maximum acceptable downtime). These objectives will heavily influence your chosen DR strategy.
-
Data Replication: Choose appropriate data replication methods based on your RPO requirements:
- Synchronous Replication: Data is written to both primary and secondary regions simultaneously. This offers near-zero RPO but can introduce latency. Services like Amazon Aurora Global Database utilize this approach.
- Asynchronous Replication: Data is written to the primary region first and then replicated to the secondary region with a slight delay. This offers lower latency but a potentially higher RPO. Services like cross-region snapshots for Amazon EBS and cross-region replication for Amazon S3 fall into this category.
- Failover Mechanisms: Determine how you will initiate and manage the failover process:
- Manual Failover: Requires human intervention to trigger the switch to the secondary region. This is suitable for less critical applications or scenarios where careful orchestration is needed.
- Automated Failover: Uses monitoring services and automation to automatically initiate failover based on predefined triggers (e.g., loss of connectivity or health check failures). AWS Route 53 health checks and DNS failover are crucial components here.
- Failback Procedures: Plan how you will return operations to the primary region once it recovers. This involves synchronizing data back, testing, and switching traffic back gracefully.
-
DR Drills and Testing: Regularly test your DR plan to identify weaknesses and ensure that your recovery procedures work as expected. Think of this as a fire drill for your IT infrastructure.
Practical Examples and Use-Cases
Let’s consider a few practical scenarios:
- Web Application with Database:
- Strategy: Active-Passive with asynchronous database replication using Amazon RDS cross-region replicas and S3 cross-region replication for static assets.
- Failover: Route 53 DNS failover to switch traffic to the standby application load balancer in the secondary region.
- Analogy: Imagine two identical websites hosted in different cities, with their databases constantly sending updates to each other with a slight delay. If one city experiences a major power outage, the traffic is automatically redirected to the website in the other city.
- Critical Financial Application with Strict RPO/RTO:
- Strategy: Active-Active with synchronous database replication using Amazon Aurora Global Database and global endpoints for application traffic.
- Failover: Aurora Global Database provides automatic failover in case of a primary region failure, with minimal data loss and downtime.
- Analogy: Think of two interconnected banking systems operating simultaneously in different states. Transactions are instantly recorded in both systems. If one system fails, the other seamlessly takes over without any disruption to customer service.
Step-by-Step Example: Setting up Cross-Region S3 Replication
Let’s walk through a simple example of setting up cross-region replication for an S3 bucket:
- Create Buckets: Create two S3 buckets in different AWS regions (e.g.,
primary-bucket-us-east-1andsecondary-bucket-us-west-2). -
Enable Versioning: Enable versioning on both the source and destination buckets. This is a prerequisite for cross-region replication.
-
Configure Replication Rule: In the source bucket’s management tab, create a new replication rule:
- Source bucket: Choose the current bucket.
- Destination bucket: Specify the ARN of the destination bucket in the other region.
- IAM role: AWS will guide you to create an appropriate IAM role that grants S3 permission to replicate objects.
- Optional settings: You can configure filters to replicate specific objects or prefixes.
- Test Replication: Upload an object to the source bucket. It should be automatically replicated to the destination bucket in the other region.
Key Takeaways
- Multi-region DR provides the highest level of resilience against large-scale outages.
- Clearly define your RPO and RTO to guide your DR strategy.
- Choose appropriate data replication methods (synchronous or asynchronous) based on your RPO.
- Implement robust failover and failback mechanisms, considering both manual and automated approaches.
- Regular DR drills are crucial to validate your plan’s effectiveness.
- AWS offers a range of services and features to facilitate multi-region DR, such as cross-region replication, global databases, and DNS failover.
Designing a robust multi-region disaster recovery plan on AWS is an investment in the long-term availability and resilience of your critical applications and data. By understanding the key concepts, leveraging the right AWS services, and rigorously testing your plan, you can significantly minimize the impact of disruptive events and ensure business continuity.